목차
Testing stochastic AI models with Hypothesis
Example-based testing - issues
- Test exhaustiveness depends on the developer
- Edge case coverage
- Time consuming
- Non-robust test
- Unclear or ambiguous function requirement
- What kind of input our function should expect?
- How the function should behave in unexpected input scenarios?
def merge_sort(list1, list2):
merged_list = list1 + list2
return sorted(list(dict.fromkeys(merged_list)))
- What data types in list should the function support?
- Are mixed data types a valid input?
- How the function should behave if it gets null as input?
Property-based testing
- Define the possible inputs
- Define the properties of the output
- Generate random examples
- Test the properties are met.
- Generalize the scenarios
- Find essential features
- Run many different inputs per property
- Find a failing edge case
- Automates writing tests
- Focus on the general claim
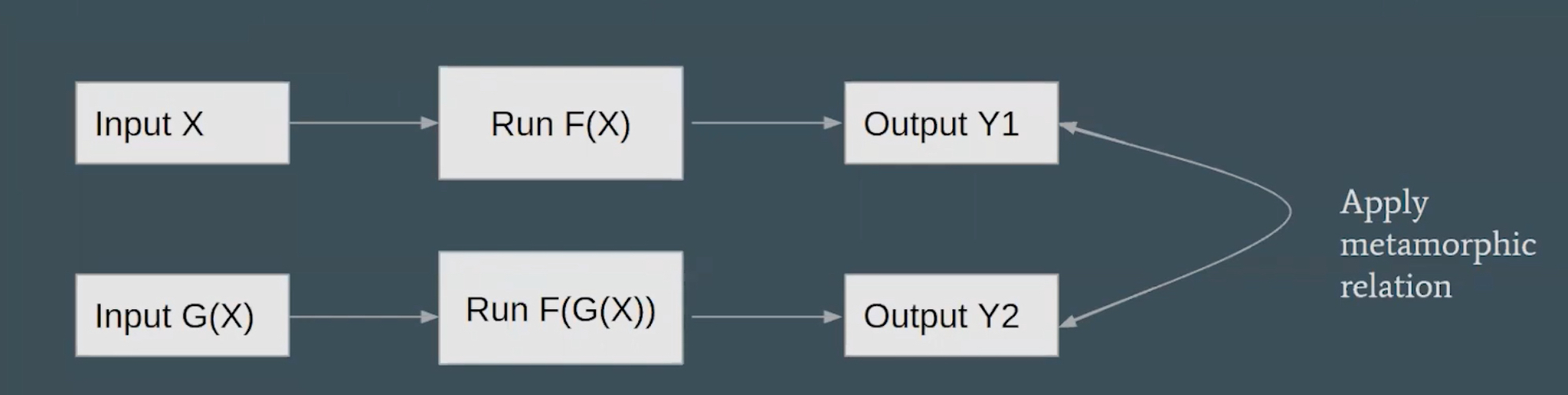
Metamorphic Testing
- Approach to address the test oracle problem and test case generation problem
- Intorduced by T.Y. Chen in 1998
- Approach to test Machine learning (Xie et al., 2010)
- Predict the output
- Metamorphic relations
- Xie et al. (2010) defined the following MRs for machine learning:
- MR-0: Consistence with affine transformation
- MR-1.1: Permutation of class labels
- MR-1.2: Permutation of the attribute
- MR-2.1: Addition of uninformative attributes
- MR-2.2: Addition of informative attributes
- MR-3.1: Consistence with re-prediction
- MR-3.2: Additional training sample
- MR-4.1: Additional of classes by duplicating samples
- MR-4.2: Additional of classes by re-labeling samples
- MR-5.1: Removal of classes
- MR-5.2: Removal of samples
Overview of Hypothesis library
Hypothesis Library
- A library designed to help write property-based tests.
- The key object of Hypothesis is a strategy.
- A strategy - a recipe for generating data
- Easy to use predefined strategies
- Focuses on finding edge cases
- Custom strategies.
@given(st.integers(), st.integers())
def test_given_integers_add_is_commutative(x, y):
assert x + y == y + x
@given(st.floats(allow_nan=False, allow_infinity=False), st.floast(allow_nan=False, allow_infinity=False))
def test_given_floats_add_is_commutative(x, y):
assert x + y == y + x
Hypothesis basic strategies
- booleans(), text(), integers(), none(), one_of(), dates(), dictionaries(), just(), permutations() and more.
@given(arrays(int, st.shared(array_shapes(min_dims=3, max_dims=5), key="shape")), arrays(int, st.shared(array_shapes(min_dims=3, max_dims=5), key="shape")))
def test_given_arrays_multiply_is_commutative(arr1, arr2):
np.array_equal(arr1 * arr2, arr2 * arr1)
- data()
@given(array_shapes(min_dims=3, max_dims=5), st.data())
def test_given_arrays_multiply_is_commutative(arr_shape, data):
arr1 = data.draw(arrays(int, arr_shape))
arr2 = data.draw(arrays(int, arr_shape))
np.array_equal(arr1 * arr2, arr2 * arr1)
merge_sort test
@given(st.lists(st.integers() | st.floats(allow_nan=False)), st.lists(st.integers() | st.floats(allow_nan=False)))
def test_commutativity(list1, list2):
assert merge_sort(list1, list2) == merge_sort(list2, list1)
Define you own strategy
- builds(target, /, *args, **kwargs) ~ pass generated args to callable
- flatmap ~ chain strategies together
- Composite strategies ~ create custom strategies
- Transforming data functions:
- Mapping
- Filtering
class Rectangle:
""" A class of Python object that describe the properties of a rectangle """
def __init__(self, width, height, center=(0, 0)):
self.width = width
self.height = height
self.center = center
def __repr__(self):
return "Rectangle(width={w}, height={h}, center={c})".format(h=self.height, w=self.widht, c=self.center)
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.get_area() < other.get_area()
def get_area(self):
return self.with * self.height
def rectangle_list_strategy():
return st.lists(st.builds(Rectangle, st.integers(min_value=0), st.integers(min_value=0), st.tuples(st.integers(), st.integers())))
@given(rectangle_list_strategy())
def test_given_rectangle_list_sort_is_distinct(rectangle_list):
assert sorted(rectangle_list) == sorted(sorted(rectangle_list))
Transforming data functions
Filtering
@given(st.integers().filter(lambda num: num % 2 ==0))
def test_given_even_number_transform_is_even(num):
assert (num + 2) % 2 == 0
Mapping
@given(st.integers().map(lambda num: num * 2))
def test_given_even_numbers_transform_is_even(num):
assert (num + 2) % == 0
Debug hypothesis strategies
- example() - return example value of strategy.
def list_strategy():
return st.lists(st.one_of(st.integers(), st.floats(allow_nan=False)))
- note() ~ print additional information on failure
- @settings decorator ~ tweak hypothesis defults
- max_examples ~ the default is 100.
- database ~ the default storage is a directory structure, located in .hypothesis/examples
- verbosity
- ~~hypothesis~show~statistics
Repeatable random testing
- A test can run successfully a couple of times before finding a failing example
- Repeat failing with the same example
- Local test database
- A bug will never go away by chance
Shrinking
- Product human readable examples
- Turn complex example into a simpler one
- Each strategy defines an order in which it shrinks
- Example: booleans() shrink towards False
Additional Components
from scipy import ndimage
from hypothesis.extra.numpy import arrays, array_shapes
@composite
def add_additional_blobs_to_prediction_strategy(draw, blob_prediction):
dilated_blob_mask = ...
...
return prediction
@given(arrays(bool, array_shape(min_dims=3, min_side=10)), st.data())
def test_given_prediction_adding_blobs_return_include_features(raw_prediction, data):
modified_prediction = data.draw(add_additional_blobs_to_prediction_strategy(raw_prediction))
assert np.all(np.isin(extract_blob_mask_features(raw_prediction), extract_blob_mask_features(modified_prediction)))
Source
Links
관련 문서
Plugin Backlinks: 아무 것도 없습니다.